 Past Research(2011-2018)
Past Research(2011-2018)
 Target Cell Types
Target Cell Types
| Team Kanai | |
| Liver | Hepatocyte Hepatic stem cell Kupffer cell Sinusoidal endothelial cell |
| Large intestine | Absorptive epithelial cell of the ascending colon Absorptive epithelial cell of the descending colon Absorptive epithelial cell of the rectum |
| Stomach | Surface epithelial cell Mucous neck cell Fundic gland |
| Kidney | Proximal tubules Distal tubules |
| Team Sasaki | |
| Placenta | Cytotrophoblast (first trimester) Cytotrophoblast (term) Syncytiotrophoblast (first trimester) Syncytiotrophoblast (term) Extravillous trophoblast (first trimester) |
| Uterus | Endometrial epithelial cell (follicular phase) Endometrial epithelial cell (secretory phase) Endometrial stroma cell |
 Team Kanai
Team Kanai
Reference epigenome analysis in normal epithelial cells of human digestive and urinary system and development of analysis technology
Yae Kanai
Professor, Keio University School of Medicine
Deputy Director, National Cancer Center Research Institute

Overview
The aim of this study is to contribute to the International Human Epigenome Consortium (IHEC), which has been established to comprehensively characterize the standard epigenome profiles of multiple normal cell lineages from different human populations, as one of several Japanese member teams supported by the Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST) division of the Japan Science and Technology (JST) Agency. We are attempting to reveal the whole picture of mechanisms regulating gene expression, e.g. DNA methylation, chromatin modifications, and abundance of each RNA species, of normal epithelial cells of the digestive system, e.g. the stomach, colon and liver, and the urinary system, e.g. the kidney, from multiple Japanese people. Quality viable cells are purified from surgically resected materials from patients who provided written informed consent in National Cancer Center Hospital, Tokyo (Figure 1). In addition, we are developing and improving innovative technologies, e.g. the post-bisulfite adaptor-tagging (PBAT) method for whole-genome bisulfite sequencing. Reference epigenome database by IHEC will promote the innovation of diagnosis and therapy of human diseases through the efficient identification of disease-specific epigenome profiles.
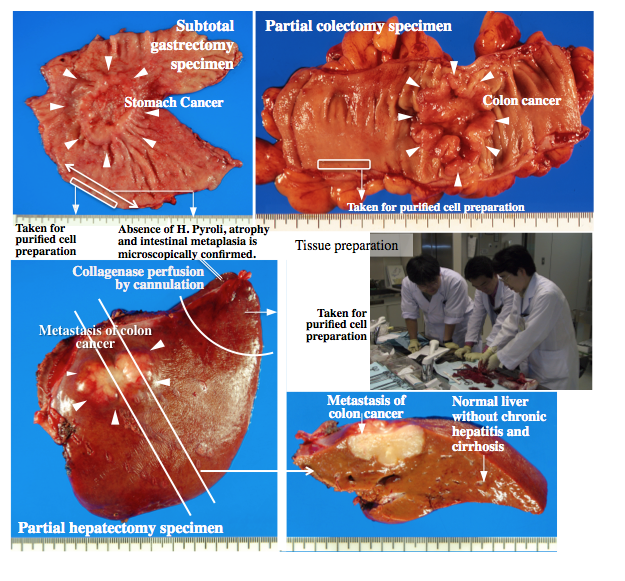
Figure 1 Surgically resected materials
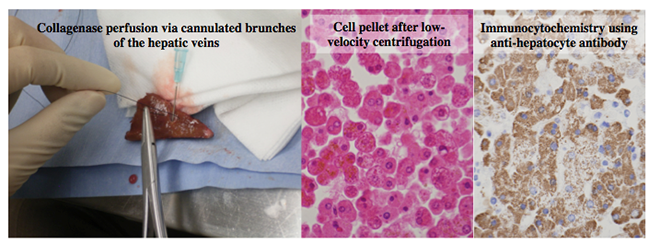
Figure 2 Purification of hepatocytes from partial hepatectomy specimens
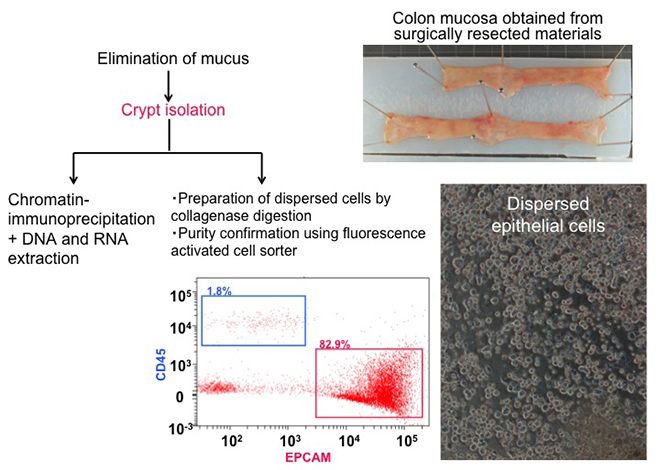
Figure 3 Purification of epithelial cells from partial colectomy specimens
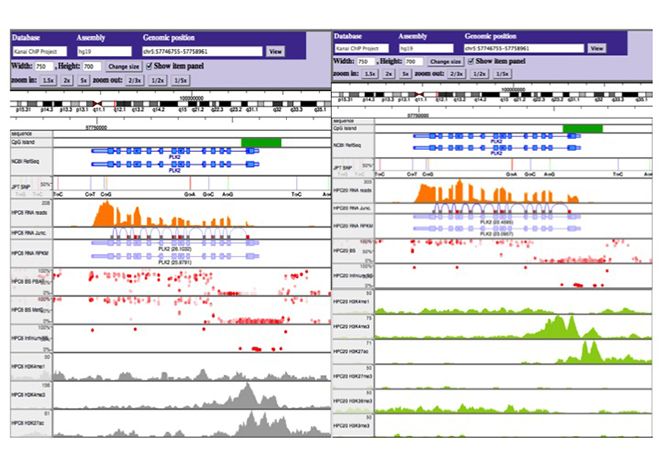 Figure 4 Originally developed browsing system
Figure 4 Originally developed browsing system
Members
Project Team Leader
- Yae Kanai
Deputy Director, Chief, Division of Molecular Pathology, National Cancer Center Research Institute
Project Group leaders
- Tatsuhiro Shibata
Chief, Division of Cancer Genomics, National Cancer Center Research Institute - Takashi Ito
Professor, Department of Biochemistry, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University - Yutaka Suzuki
Associate Professor, Human Genome Center, The Institute of Medical Science, University of Tokyo
 Team Shirahige
Team Shirahige
Development of genomic technologies to explore human epigenetic regulation
Katsuhiko Shirahige
Professor, University of Tokyo

Overview
Our body consists of more than 250 cell types. While each cell has the same DNA sequence, protein modifications and their binding pattern(so called epigenetic information)defines the specificity of each cell type. The aim of this study is to develop the new standard method to analyze whole picture of epigenetic information and use the method to explore whole-genome epigenetic information of various endothelial cell species. Our ultimate goal is to contribute to the International Human Epigenome Consortium through both epigenomics data and technology development. These data and methods are expected to contribute to basic research and drug discovery as well.
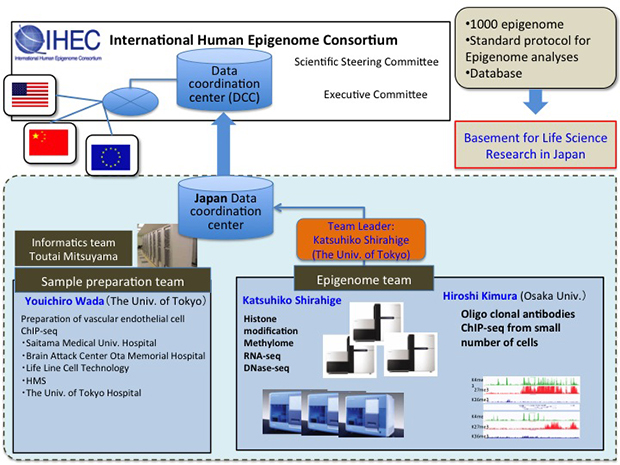
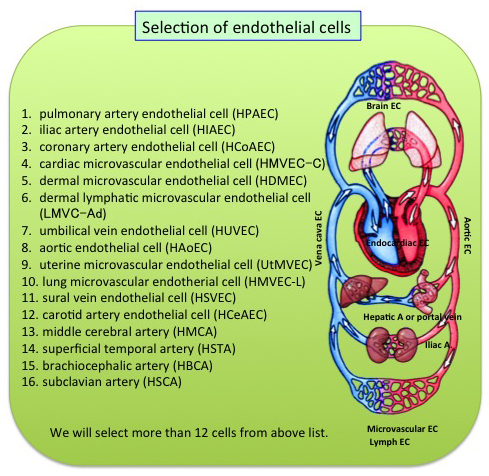
Members
Project Team Leader
- Katsuhiko Shirahige
Professor, Laboratory of Genome Structure and Function, Research Center for Epigenetic Disease, University of Tokyo
Director of Research Center for Epigenetic Disease
Project Group leaders
- Youichiro Wada
Professor, Systems Biology and Medicine, Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology (RCAST), University of Tokyo - Hiroshi Kimura
Associate Professor, Biomolecular Networks Laboratories Nuclear Dynamics Group, Graduate School of Frontier Biology, Osaka University - Toutai Mituyama
Research Scientist, Computational Biology Research Center (CBRC), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Tokyo
 Team Sasaki
Team Sasaki
Epigenomic analysis of the human placenta and endometrium constituting the fetal-maternal interface
Hiroyuki Sasaki
Distinguished Professor and Director, Kyushu University

Overview
This study aims to determine the reference epigenomes of the human placenta and endometrium, which constitute the fetal-maternal interface, for future use in studies of human diseases associated with reproduction and development. In the placenta, we focus on cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast cells (both at first trimester and at term) and, in the endometrium, we focus on epitherial cells (at the follicular and secretory phases) and stroma cells. To this end, we will develop and establish the technologies to isolate these cells and analyze the epigenomic modifications. We will further try to determine the epigenomes of disease samples, such as pregnancy-induced-hypertension placentae, hydatidiform moles, and endometriosis specimens, to search for disease-specific changes. We will also determine the methylomes of sperm from oligospermic patients for their use in the improvement of assisted reproductive technology.
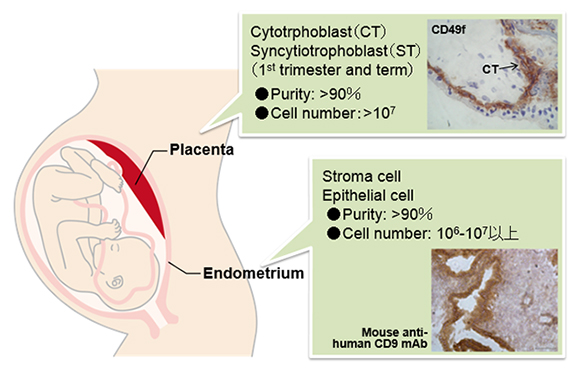
Figure 1 Optimization of procedures for cell isolation from the placenta and endometrium
Members
Project Team Leader
- Hiroyuki Sasaki
Professor, Division of Epigenomics and Development, Medical Institute of Bioregulation, Kyushu University
Director of the Medical Institute of Bioregulation
Project Group leaders
- Takahiro Arima
Professor, Department of Development and Environmental Medicine, Tohoku University - Kenichiro Hata
Director, Department of Maternal-Fetal Biology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development, Tokyo - Mikita Suyama
Professor, Division of Bioinformatics, Medical Institute of Bioregulation, Kyushu University